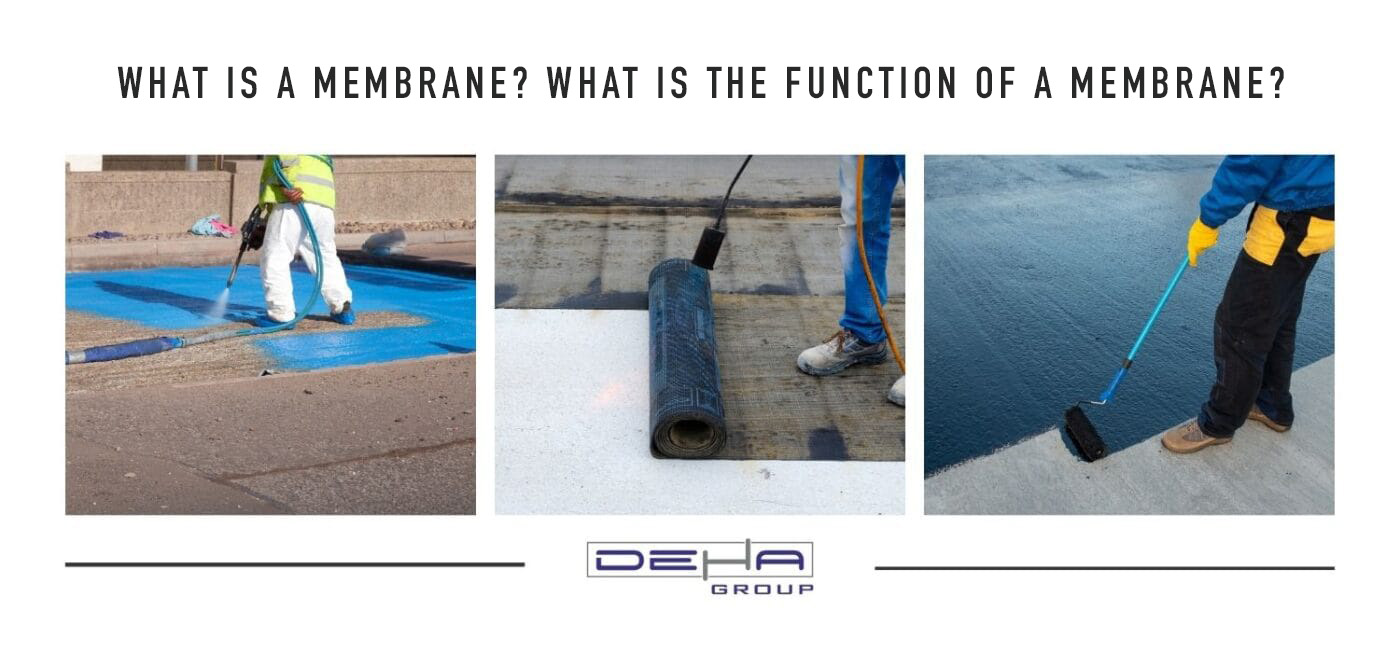
A membrane is a thin, flexible layer typically used to protect a surface or provide sealing. Widely used in industrial fields, this material is produced with various chemical and physical properties. Membranes can be made from polymers, rubber, plastic, or synthetic materials, providing protection against both liquid and gas leakage. They are particularly preferred in water insulation, wastewater management, construction, and energy sectors.
One of the most important features of membranes is their durability. They resist high heat, chemicals, and physical pressures. Therefore, they offer a long-lasting solution against external factors and increase the durability of structures. Thanks to the technologies used in production processes, the thickness and material components of membranes can be adjusted according to their area of use.
Membranes produced with modern technologies are widely used in various applications and, thanks to their advanced features, offer both protective and functional solutions. These materials stand out as reliable insulation materials, especially in industrial facilities and large infrastructure projects.
Membranes are generally used to prevent the leakage of water and other liquids. Membranes used for waterproofing can be applied at many points, from the foundations of buildings to the roofs. In this way, structures are protected against damage that could result from moisture and water. For example, membranes prevent water from seeping into concrete structures, extending the lifespan of these structures. This material, frequently preferred in the construction industry, stands out for its waterproofing feature.
In industrial facilities, membranes are used to prevent the leakage or spread of chemical substances. In chemical factories, energy plants, and waste management areas, such membranes prevent hazardous substances from spreading to the environment. They also contribute to reducing energy costs by providing energy efficiency.
Membranes are also used to minimize damage that could result from environmental factors. For example, membranes resistant to sunlight and extreme heat provide a significant advantage for structures used in open areas. This material provides economical protection for structures by ensuring long-term cost savings.

There are various types of membranes designed for different applications. Among the most preferred membranes for waterproofing are bituminous membranes and PVC membranes. Bituminous membranes form a solid surface by adhering with hot air sources, while PVC membranes can be easily applied to different parts of buildings due to their flexible structure. Both types offer high performance in terms of waterproofing and durability.
The membranes used in industrial areas are produced to be resistant to chemicals and high temperatures. These types of membranes are commonly used in high-risk areas such as oil refineries, chemical storage facilities, and power plants. Chemically resistant membranes play a crucial role in preventing the leakage of hazardous substances, thus contributing to environmental protection.
In the agricultural sector, membranes are of great importance for water management. Waterproof membranes used in irrigation ponds prevent water from seeping into the ground, thereby saving water. They also prevent harmful agricultural chemicals from mixing with groundwater, thus preserving both environmental quality and product quality.
One of the greatest advantages of membranes is that they offer a long-lasting and durable solution. Due to their high resistance, they provide effective protection against external factors for an extended period. Additionally, the maintenance costs of these materials are low, as membranes can typically last for many years without needing frequent replacement. This offers cost savings for both construction and industrial projects.
Moreover, membranes are also known as environmentally friendly materials. They help conserve natural resources and increase energy efficiency. Membranes used in building insulation, in particular, reduce energy consumption, lowering heating and cooling costs. This is a sustainable solution both environmentally and economically.
Lastly, membranes offer flexible use in various projects. These materials are produced in different thicknesses and types and can be customized according to the area of application. Thanks to their flexible structures, they can easily adapt to different surfaces of buildings and offer a wide range of applications.

 TR
TR