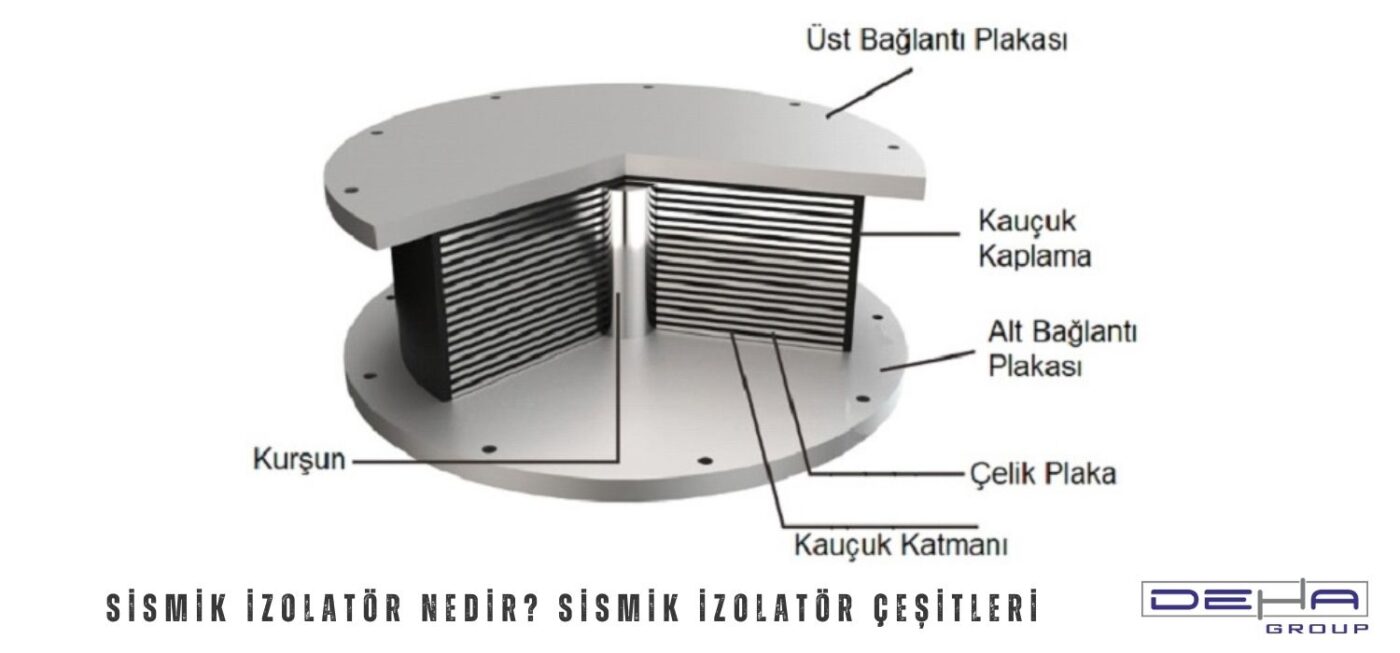
Seismic isolators are structural elements developed to enhance the resilience of buildings and bridges against ground motions such as earthquakes. These systems play a crucial role in building safety by absorbing horizontal movements caused by an earthquake, thereby reducing the damage to structures. They are used to diminish the energy generated during an earthquake, increasing the safety of occupants and ensuring the structure remains intact. In areas with high earthquake risk, these systems have become part of modern building standards.
Seismic isolators prevent vibrations from being directly transferred to the main structural system of the building by isolating them. These systems provide flexibility to the structure, minimizing the impact of seismic waves. By dissipating earthquake energy, they stabilize the structure and reduce potential damage. Due to these features, they are commonly used in strategic buildings like hospitals, schools, and public buildings.
The installation of seismic isolators affects all structural elements, starting from the foundation of the structure. These isolators are typically placed in the building's foundation or columns and help in diverting the effects of an earthquake away from the building. Therefore, seismic isolators protect not only the structural safety but also the functionality and post-earthquake usability of the building.
There are different types of seismic isolators, each with its unique advantages. These types are chosen based on the structure type, soil structure, and expected seismicity level. Seismic isolators can be generally categorized into elastomeric isolators, sliding isolators, and hybrid systems.
Elastomeric Isolators
Elastomeric isolators consist of rubber layers combined with steel plates. While the rubber provides flexibility to the structure, the steel plates enhance durability. Elastomeric isolators, which damp horizontal movements during an earthquake, are commonly used in high-rise buildings. Thanks to the rubber component, the isolator absorbs vibrations from the ground, ensuring the safety of the structure. Elastomeric isolators are often one of the most frequently used types of seismic isolators.
Sliding Isolators
Sliding isolators are equipped with special materials that allow movement between the structure and the ground. Placed at the base of the structure, this system allows the building to slide, reducing the impact of the earthquake. The main purpose of sliding isolators is to minimize horizontal movements from the ground and keep the structure more secure. These types of isolators are generally preferred in structures and bridges where a higher degree of sliding movement is required during an earthquake.
Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems are a combination of elastomeric and sliding isolators. These systems combine the flexibility of elastomeric isolators with the sliding capacity of sliding isolators. Thus, they provide more effective protection against the effects of the earthquake at different frequencies. Hybrid systems offer an ideal solution for large structures and are especially preferred for buildings like hospitals, schools, and bridges. These types of systems provide a stronger defense against the earthquake's effects in different directions.
Seismic isolators contribute greatly to building safety. These systems, which do not directly transmit seismic energy to the structure during earthquakes, help prevent both structural damage and potential loss of life. In particular, the use of seismic isolators is of great importance for structures with critical functions after an earthquake. Thanks to these systems, the building becomes safer, protected from the effects of the earthquake, and can continue to function.
These isolators absorb vibrations by increasing the flexibility of the structure. They prevent unnecessary stress on building materials, providing long-lasting protection. This reduces both short-term and long-term costs for buildings and lowers maintenance requirements. Additionally, equipment and furniture inside the building are minimally affected during an earthquake, providing advantages in terms of interior safety as well as structural integrity.
The use of seismic isolators is one of the most important elements of modern construction engineering. Especially in high-risk earthquake areas like Turkey, the widespread implementation of seismic isolators is a significant step for community safety.
Seismic isolators are used in a variety of structures, especially in areas with a high risk of earthquakes. These systems are widely applied not only in buildings but also in strategic structures like bridges, viaducts, hospitals, and public buildings. Isolators used in public buildings ensure that these structures can continue to operate safely during emergencies. In hospitals, they are chosen to prevent damage to medical equipment and interruptions to healthcare services due to the effects of earthquakes.
Seismic isolators used in bridges and viaducts make these structures earthquake-resistant and contribute to the safe continuation of transportation after an earthquake. Structural damage to bridges can lead to loss of life and disrupt transportation. Therefore, seismic isolators are of vital importance in bridge structures.
Moreover, the use of seismic isolators in residential projects is becoming increasingly common. They are preferred in high-rise buildings and luxury residential projects to enhance structural safety. In this way, the security of individual living spaces is ensured, providing residents with a more protected life in areas with a high risk of earthquakes.

 TR
TR