HEA steel is one of the types of steel profiles widely used in the construction industry. These profiles, noted for their lightweight structure, durability, and design flexibility, are among the top choices in various projects. HEA steel is known for carrying structural loads, constructing durable buildings, and providing solutions in steel construction projects. So, what is HEA steel, how is it produced, and in which areas is it used?
HEA steel takes its name from the initials of the words Harf and Endürans, and is defined among steel profiles by its "H" shaped cross-section. These profiles are generally prominent in building and infrastructure projects. The main features of HEA steel used in the construction sector are as follows:
It offers a lightweight and versatile design.
It has high strength due to its uniform cross-section.
It provides easy assembly and installation.
HEA steel offers a more suitable alternative for lightweight projects compared to other steel profile types like HEB and IPE.
HEA steel production encompasses steel casting and shaping processes. The main stages of these processes are as follows:
Raw Material Preparation: The primary materials used in HEA steel production are iron ore and recycled steel. These raw materials are conditioned for steel casting in furnaces.
Casting and Shaping: The obtained liquid steel is shaped into HEA profiles using special molds. At this stage, the profiles are given the desired dimensions and sectional properties.
Cooling and Annealing: The shaped profiles are cooled in a controlled manner, and their strength is increased through annealing.
Cutting and Finishing: The profiles are cut to the desired dimensions, and surface cleaning processes are applied. This stage ensures the products are ready for use.
Applications of HEA Beams
HEA beams are commonly used in the following areas:
Construction and Building Sector:
They are used to ensure durability in building columns and beams.
They are among the main load-bearing elements in steel structures of industrial buildings.
Bridge and Infrastructure Projects:
HEA beams are used in the construction of bridge piers and platforms.
Preferred in infrastructure projects due to their high strength and durable structure.
Machinery and Industrial Facilities:
HEA profiles play an important role in machine chassis and the internal structures of industrial facilities.
Decoration and Architectural Applications:
Combines aesthetics and durability in special design projects.
Differences Between HEA, HEB, and IPE Beams
HEA beams have different characteristics compared to HEB and IPE beams. The main differences are as follows:
Cross-Sectional Dimensions: HEA profiles have lighter cross-sectional dimensions than HEB profiles. Therefore, they are preferred in projects where high load-bearing capacity is not required.
Weight: HEA beams are lighter than HEB and offer a wider section compared to IPE profiles.
Applications: While HEB profiles have a higher load-bearing capacity, HEA profiles offer a more economical option for lightweight projects. IPE is generally used in flooring applications.
Materials Used in the Production of HEA Beams
The main materials used in the production of HEA beams are:
Carbon Steel: Provides durability and strength.
Alloy Steel: Preferred for its corrosion-resistant structure.
Stainless Steel: Used in projects that require aesthetics and longevity.
The material properties of HEA beams are specially optimized during the production process, ensuring durable performance under various climatic conditions.
Rolling and Shaping Techniques for HEA Beams
HEA beams are widely used in the steel construction sector and are preferred for building durable structures due to their high strength. Rolling and shaping techniques play an important role in their production. Steel is rolled at high temperatures to achieve the desired shape. The following techniques are prominent in this process:
Hot Rolling: HEA beams are generally produced by hot rolling. In this method, the steel is shaped by heating it above its recrystallization temperature, improving mechanical properties and minimizing surface defects.
Cold Rolling: Preferred for more precise tolerances and better surface quality. However, this method can increase the hardness of the steel and extend the shaping process.
Mold Shaping: During the rolling process, HEA beams are standardized using special molds designed to fit the unique dimensions and shapes of HEA profiles.
The rolling and shaping process of HEA beams must be conducted carefully to reduce production costs and optimize the durability of the steel materials.
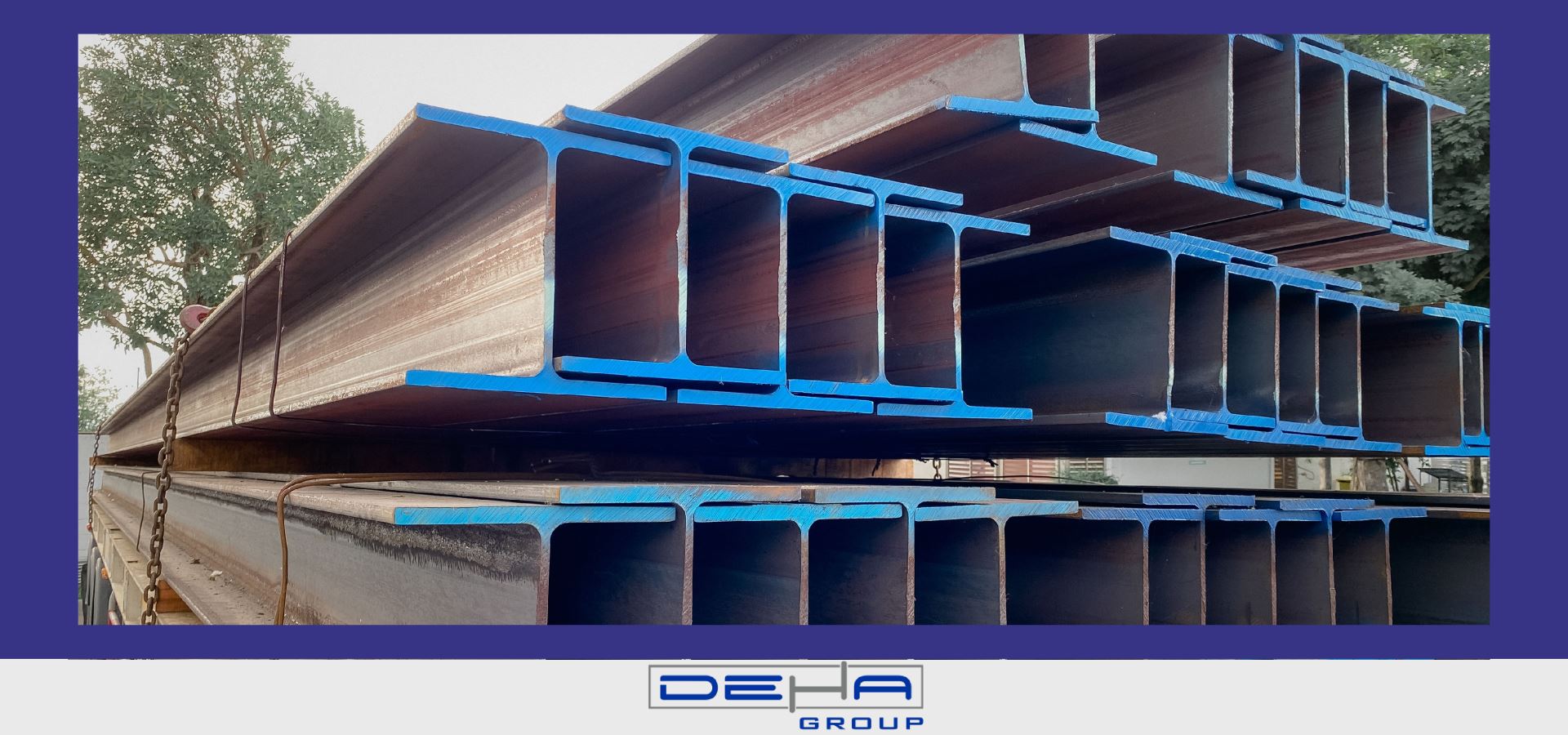

Welding and Assembly Techniques for HEA Beams
The assembly and welding techniques of steel structures using HEA beams play a critical role in building durable and long-lasting structures. The following methods are commonly used in welding and assembly:
MIG/MAG Welding: This method, widely used in welding HEA beams, offers a fast and efficient solution.
TIG Welding: Preferred for more precise work. This method meets the requirements for fine and detailed welding.
Bolted Assembly: The use of bolts and nuts is common in assembling HEA beams in large steel structures. This method provides ease of disassembly if necessary.
Flange Connection: Flanges shaped between HEA beams enhance both the durability and flexibility of steel structures.
During the welding and assembly process, the dimensions and design characteristics of HEA beams must be considered in advance planning to ensure the longevity and durability of the structures.
Considerations in Designing Steel Structures with HEA Beams
Proper material selection and design planning are critical in designing steel structures with HEA beams. Points to consider during these stages:
Load-Bearing Capacity: HEA beams have a high load capacity as the structural elements of buildings. Therefore, pre-analysis should be performed in the design.
Corrosion Resistance: Corrosion protection is necessary for the longevity of steel structures. HEA beams are typically protected by galvanizing or special coatings.
Connection Points: Connection details determine the stability of the structure. Correct bolt and welding techniques should be used.
Aesthetics and Functionality: HEA beams support modern designs in steel structure elements. A balance between aesthetics and functionality should be achieved in design.
These criteria ensure both durability and longevity in steel structure projects with HEA beams.
Export Opportunities and Competitive Analysis of HEA Profiles
HEA beams are notable as a significant export item in the steel industry. To understand export opportunities and competitive conditions, the following factors should be evaluated:
Target Markets: European, Middle Eastern, and Asian markets play an important role in the export of HEA beams. Increasing infrastructure investments in these regions are raising demand.
Standards and Certifications: Producing HEA beams in compliance with international standards provides a competitive advantage. Quality certificates like CE certification are important in exports.
Price Competition: Fluctuations in steel prices can affect exporters. Efficient production and logistics planning can provide cost advantage.
Logistics and Distribution: As HEA beams are heavy and bulky products, logistics processes play a critical role. Economic transportation alternatives like sea routes can reduce costs.
Proper evaluation of these factors helps HEA beams remain competitive in international markets.
Dimensions and Standards of HEA Beams
HEA beams come in various sizes and standards for use in different projects. Important dimensions and standards include:
Dimensions: HEA profiles typically have a cross-sectional width ranging from 100 mm to 1000 mm. This variety offers flexibility in steel structure designs.
Standards: HEA beams are produced according to European standards such as EN 10025 and EN 10034. These standards determine dimension tolerances and material quality.
Weights: Their weights vary depending on the length and size of the profile. Therefore, size selection should be made according to project requirements.
Coating Options: HEA beams are generally galvanized or painted for corrosion protection. This feature enhances longevity.
The dimensions and standards of HEA beams allow for designs tailored to the specific requirements of projects. Therefore, the technical characteristics of HEA beams should be accurately analyzed in projects.

 TR
TR